Polygenic risk scores predict diabetes complications and their response to intensive blood pressure and glucose control
Johanne Tremblay, Mounsif Haloui, […] Pavel Hamet
Diabetologia (2021) | Cite this article
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis
Type 2 diabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular and renal complications, but early risk prediction could lead to timely intervention and better outcomes. Genetic information can be used to enable early detection of risk.
Methods
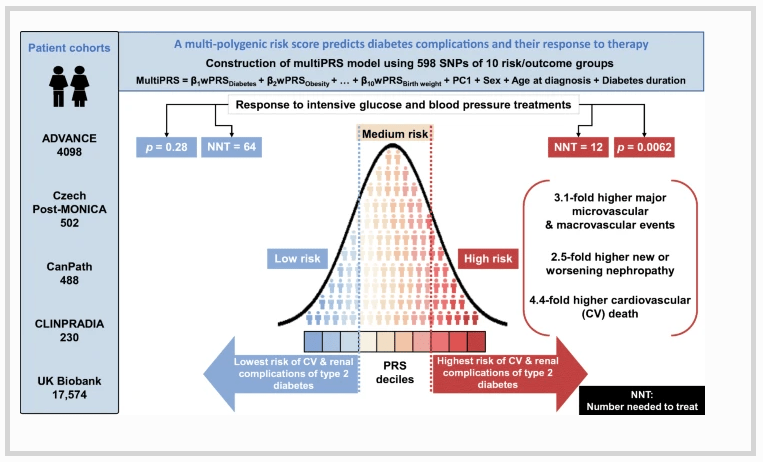
We developed a multi-polygenic risk score (multiPRS) that combines ten weighted PRSs (10 wPRS) composed of 598 SNPs associated with main risk factors and outcomes of type 2 diabetes, derived from summary statistics data of genome-wide association studies. The 10 wPRS, first principal component of ethnicity, sex, age at onset and diabetes duration were included into one logistic regression model to predict micro- and macrovascular outcomes in 4098 participants in the ADVANCE study and 17,604 individuals with type 2 diabetes in the UK Biobank study.
Results
The model showed a similar predictive performance for cardiovascular and renal complications in different cohorts. It identified the top 30% of ADVANCE participants with a mean of 3.1-fold increased risk of major micro- and macrovascular events (p = 6.3 × 10−21 and p = 9.6 × 10−31, respectively) and a 4.4-fold (p = 6.8 × 10−33) higher risk of cardiovascular death. While in ADVANCE overall, combined intensive blood pressure and glucose control decreased cardiovascular death by 24%, the model identified a high-risk group in whom it decreased the mortality rate by 47%, and a low-risk group in whom it had no discernible effect. High-risk individuals had the greatest absolute risk reduction with a number needed to treat of 12 to prevent one cardiovascular death over 5 years.
Conclusions/interpretation
This novel multiPRS model stratified individuals with type 2 diabetes according to risk of complications and helped to target earlier those who would receive greater benefit from intensive therapy.
Graphical abstract